Nová publikace se spoluautorstvím Františka Karlického a Masouda Shahrokhiho!
First-principles investigation of novel stable, strong, and highly attractive semiconducting nanoporous C3N and CN monolayers
Odkaz zde: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2026.103088
Abstrakt:
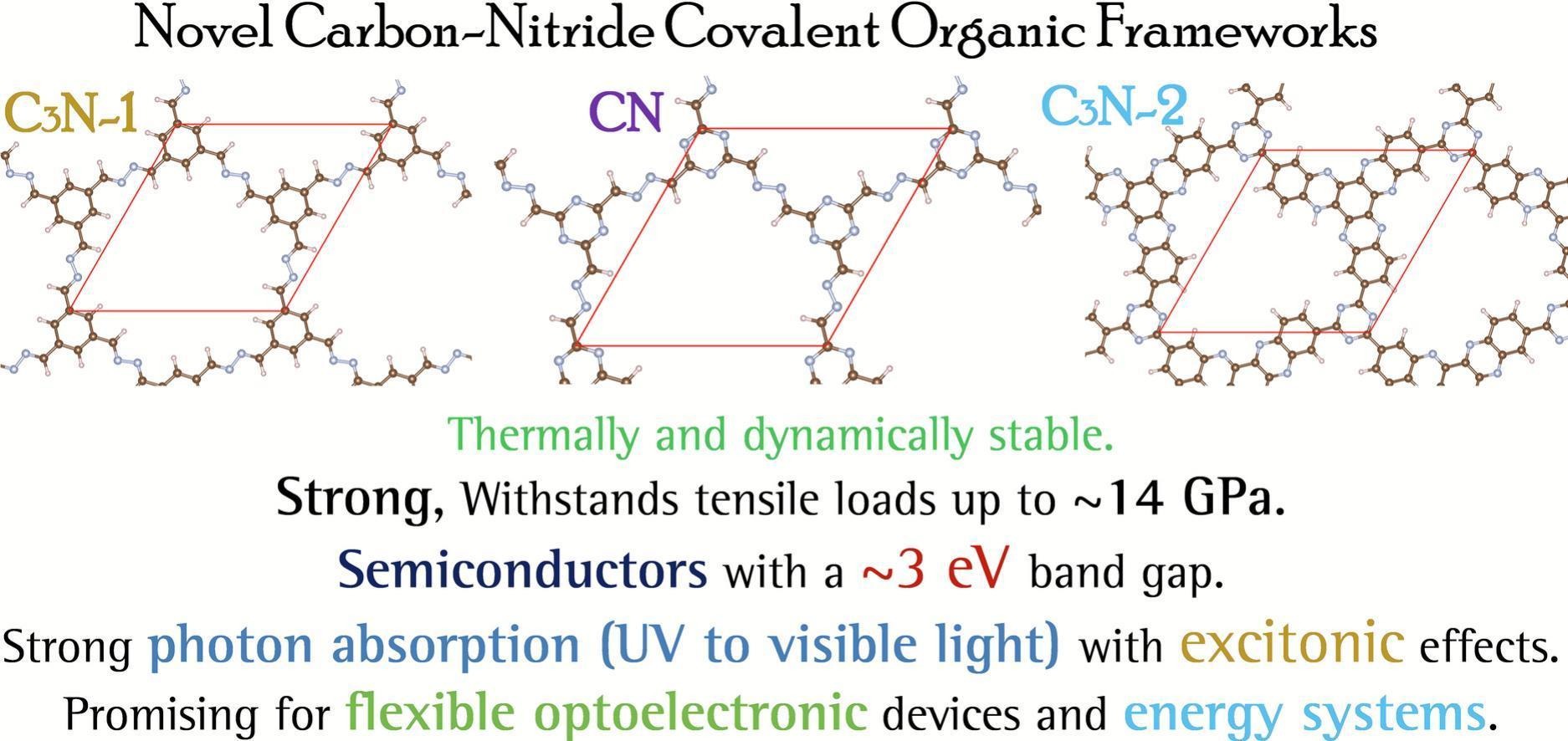
In recent breakthroughs in the field of nanoporous carbon-nitride two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials, two novel covalent organic frameworks (COFs) with a C3N stoichiometry (J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 18151 & Angew. Chem. 2024, 136, e202415624) have been synthesized. Based on the realized C3N lattices, we also designed a new COF with CN stoichiometry and s-triazine core molecules. First-principles calculations based on the density functional theory and machine learning interatomic potentials were performed to investigate the dynamical and thermal stability, electronic band structure, optical, excitonic and mechanical properties of the free-standing C3N and CN monolayers. The results demonstrate remarkable thermal and dynamical stability of the C3N and CN nanosheets. Additionally, despite their highly porous structures, the C3N and CN monolayers are predicted to be able to withstand high tensile loads up to approximately 14 GPa. Electronic band structure calculations using the hybrid HSE06 functional indicate band gaps of around 3 eV in the considered C₃N and CN monolayers, which also lead to strong photon absorption spanning the ultraviolet to visible spectrum as well as interesting excitonic effects, highlighting their potential for optoelectronic applications. Additionally, their high work function suggests promising roles as hole injection layers in optoelectronic devices and as electron-blocking layers in energy-related applications. Presented first-principles results confirm the decent thermal/dynamical stability and mechanical robustness of semiconducting C₃N and CN nanosheets, positioning them as appealing candidates for designing flexible optoelectronic devices and high-efficiency energy storage/conversion systems.